Introduction
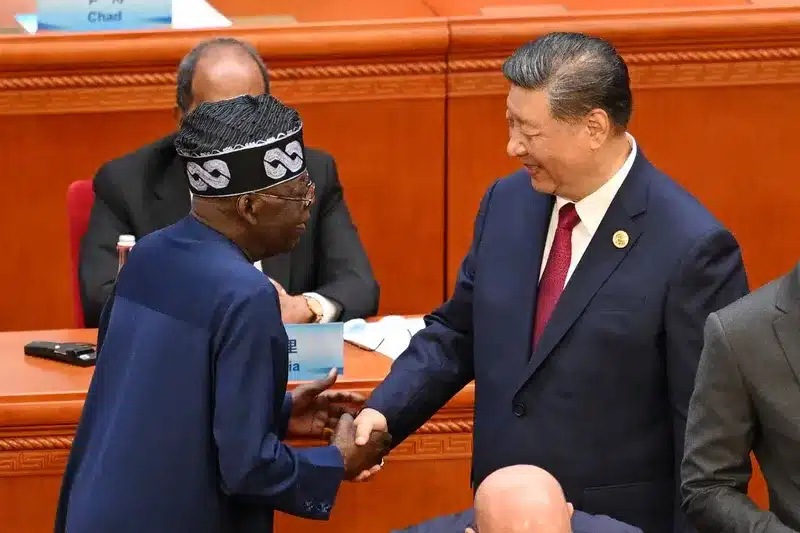
China’s relationship with Africa has evolved into one of the most strategically significant partnerships in the global South. This connection, underpinned by economic, political, and cultural ties, has seen significant growth in recent years, with China positioning itself as Africa’s largest trading partner and a key investor in the continent’s development. In a landmark announcement during the 2024 Forum on China-Africa Cooperation (FOCAC), President Xi Jinping outlined China’s ambitious plan to expand its cooperation with Africa through a $51.4 billion investment by 2027. This move is part of a broader strategy to deepen ties and foster sustainable development across the continent, impacting sectors ranging from infrastructure to healthcare.
Background and Context
China’s engagement with Africa is not a recent phenomenon. Over the past two decades, the relationship has been characterized by a series of high-profile investments and projects aimed at boosting infrastructure, enhancing trade, and supporting socio-economic development. The Forum on China-Africa Cooperation, established in 2000, serves as the primary platform for dialogue and cooperation between China and African nations. It is through this forum that China has pledged substantial investments and financial support, reflecting its commitment to the continent’s development.
The 2024 FOCAC summit, held in Beijing, marked a significant milestone in this ongoing partnership. With 53 out of 54 African nations now engaged in strategic partnerships with China, the scope and depth of these relationships have reached unprecedented levels. This year’s summit saw the signing of the “Beijing Declaration on Joining Hands to Advance Modernization and Build a High-Level China-Africa Community with a Shared Future for the New Era,” a document that underscores the mutual goals of both regions.
The $51.4 Billion Investment Plan
President Xi Jinping’s announcement of a $51.4 billion investment plan is a testament to China’s long-term commitment to Africa’s development. This substantial investment is part of a broader strategy to implement ten partnership actions across various sectors, with funding expected to be fully disbursed by 2027. The investment is structured into three main components: a credit line, assistance, and direct investment by Chinese companies.
- Credit Line and Financial Assistance
China has allocated a credit line of 210 billion yuan (approximately $29.8 billion) to support infrastructure development and other critical projects across Africa. This credit line is expected to finance large-scale infrastructure projects, including roads, railways, and ports, which are essential for enhancing connectivity and facilitating trade within the continent. Additionally, 80 billion yuan ($11.3 billion) has been earmarked for assistance, which will be directed towards social and economic development programs, including healthcare, education, and poverty alleviation. - Direct Investment by Chinese Companies
Chinese companies are expected to invest 70 billion yuan ($9.9 billion) in various sectors, including agriculture, manufacturing, and technology. These investments are aimed at boosting local economies, creating jobs, and fostering sustainable development. One of the key areas of focus will be agriculture, where China plans to establish standardized agricultural demonstration areas covering more than 6,600 hectares. This initiative is expected to enhance food security and support the development of value-added agricultural products.
Healthcare Cooperation
One of the standout aspects of China’s investment plan is its focus on healthcare cooperation. The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the vulnerabilities of healthcare systems across Africa, and China’s response has been to significantly ramp up its support in this area. Under the new plan, China will send 2,000 healthcare workers to the continent and launch 20 programs aimed at improving health facilities and combating diseases such as malaria.
Malaria remains one of the most significant public health challenges in Africa, with the World Health Organization (WHO) reporting that the continent accounted for 94% of global malaria cases and 95% of malaria-related deaths in 2022. China’s commitment to combating this disease is evidenced by its plan to establish an alliance of hospitals and medical centers across Africa. These institutions will serve as hubs for malaria treatment and prevention, leveraging Chinese expertise in medical technology and healthcare management.
In addition to combating malaria, China’s healthcare initiatives in Africa will include the construction of hospitals, training of medical personnel, and the provision of medical equipment and supplies. This comprehensive approach is expected to significantly improve healthcare outcomes across the continent, particularly in rural and underserved areas.
Agriculture and Food Security
Agriculture remains the backbone of many African economies, providing employment and livelihoods for millions of people. Recognizing this, China has prioritized agricultural cooperation as a key component of its partnership with Africa. The investment plan includes the provision of 1 billion yuan ($142.1 million) for emergency food assistance to African countries facing food insecurity. This funding will be used to deliver food supplies and support nutrition programs in regions affected by drought, conflict, and other crises.
Beyond emergency assistance, China’s investment in agriculture will focus on long-term development. The establishment of agricultural demonstration areas will introduce modern farming techniques and technologies to African farmers, helping to increase productivity and food production. These areas will also serve as training centers where local farmers can learn about sustainable farming practices and gain access to improved seeds, fertilizers, and irrigation systems.
China’s agricultural initiatives will also include the deployment of 500 agricultural experts to Africa, who will work closely with local farmers and agricultural institutions. These experts will provide technical assistance, share best practices, and support the development of value chains that can enhance the competitiveness of African agricultural products in global markets. The goal is to create at least 1 million jobs through these initiatives, contributing to economic growth and poverty reduction in rural areas.
Common Security and Digital Cooperation
Security is another critical area of focus in China’s partnership with Africa. As part of the $51.4 billion investment plan, China will provide 1 billion yuan to train 6,000 military personnel and 1,000 police officers from African countries. This training will be conducted in China and will cover a range of topics, including counter-terrorism, peacekeeping, and disaster response. Additionally, China will invite 500 young African military officers to visit China as part of a cultural exchange program aimed at strengthening mutual understanding and cooperation.
In the realm of digital cooperation, China plans to establish a digital technology cooperation center in Africa. This center will oversee the implementation of 20 digital projects and 30 infrastructure connectivity projects across the continent. These initiatives are designed to enhance Africa’s digital infrastructure, improve internet connectivity, and support the development of the digital economy. By investing in digital technology, China aims to help African countries leapfrog traditional development stages and embrace the opportunities of the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
Strategic Partnerships and Diplomatic Relations
The 2024 FOCAC summit also saw the signing of strategic partnership agreements between China and several African countries. These partnerships represent the highest level of diplomatic relations between China and these nations, reflecting the deepening ties and mutual trust between the two regions.
Countries such as Libya, Mali, Comoros, Togo, Djibouti, the Seychelles, Chad, Malawi, and Mauritania upgraded their diplomatic relations with China to the level of strategic partnership. Other nations, including Nigeria and Cameroon, adopted comprehensive strategic partnerships, while South Africa signed a “new era comprehensive strategic cooperative partnership” with China, the highest level of diplomatic relations China has with any African country.
These partnerships are not just symbolic; they are designed to facilitate greater cooperation across various sectors, including trade, investment, and security. For example, the comprehensive strategic partnership between China and Nigeria is expected to result in increased Chinese investment in Nigeria’s infrastructure and energy sectors, while the strategic partnership with South Africa will focus on enhancing cooperation in science and technology, education, and cultural exchange.
The Beijing Declaration and Future Prospects
At the conclusion of the 2024 FOCAC summit, China and Africa adopted two key documents: the “Beijing Declaration on Joining Hands to Advance Modernization and Build a High-Level China-Africa Community with a Shared Future for the New Era” and the “Beijing Action Plan (2025-2027).” These documents outline the goals and objectives of the China-Africa partnership for the coming years and provide a roadmap for achieving these goals.
The Beijing Declaration emphasizes the importance of mutual respect, equality, and win-win cooperation in China-Africa relations. It also highlights the need for both regions to work together to address global challenges, such as climate change, poverty, and inequality. The declaration reaffirms China’s commitment to supporting Africa’s modernization efforts and underscores the continent’s right to pursue its development path without external interference.
The Beijing Action Plan (2025-2027) outlines specific initiatives and projects that will be implemented under the China-Africa partnership. These include infrastructure development, capacity building, cultural exchange, and environmental protection. The action plan also sets targets for increasing trade and investment between China and Africa, with a focus on reducing trade barriers and promoting greater economic integration.
Conclusion
China’s $51.4 billion investment plan for Africa represents a significant step forward in the China-Africa partnership. By focusing on critical areas such as infrastructure, healthcare, agriculture, security, and digital cooperation, China is positioning itself as a key partner in Africa’s development journey. The initiatives announced at the 2024 FOCAC summit are expected to have a lasting impact on the continent, helping to drive economic growth, create jobs, and improve the quality of life for millions of Africans.
As China and Africa continue to deepen their ties, the future of this partnership looks promising. With a shared vision of modernization and a commitment to mutual respect and cooperation, China and Africa are well-positioned to build a high-level community with a shared future for the new era.
photo source: Google
By: Montel Kamau
Serrari Financial Analyst
9th September, 2024
Article, Financial and News Disclaimer
The Value of a Financial Advisor
While this article offers valuable insights, it is essential to recognize that personal finance can be highly complex and unique to each individual. A financial advisor provides professional expertise and personalized guidance to help you make well-informed decisions tailored to your specific circumstances and goals.
Beyond offering knowledge, a financial advisor serves as a trusted partner to help you stay disciplined, avoid common pitfalls, and remain focused on your long-term objectives. Their perspective and experience can complement your own efforts, enhancing your financial well-being and ensuring a more confident approach to managing your finances.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute financial advice. Readers are encouraged to consult a licensed financial advisor to obtain guidance specific to their financial situation.
Article and News Disclaimer
The information provided on www.serrarigroup.com is for general informational purposes only. While we strive to keep the information up to date and accurate, we make no representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, about the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability, or availability with respect to the website or the information, products, services, or related graphics contained on the website for any purpose. Any reliance you place on such information is therefore strictly at your own risk.
www.serrarigroup.com is not responsible for any errors or omissions, or for the results obtained from the use of this information. All information on the website is provided on an as-is basis, with no guarantee of completeness, accuracy, timeliness, or of the results obtained from the use of this information, and without warranty of any kind, express or implied, including but not limited to warranties of performance, merchantability, and fitness for a particular purpose.
In no event will www.serrarigroup.com be liable to you or anyone else for any decision made or action taken in reliance on the information provided on the website or for any consequential, special, or similar damages, even if advised of the possibility of such damages.
The articles, news, and information presented on www.serrarigroup.com reflect the opinions of the respective authors and contributors and do not necessarily represent the views of the website or its management. Any views or opinions expressed are solely those of the individual authors and do not represent the website's views or opinions as a whole.
The content on www.serrarigroup.com may include links to external websites, which are provided for convenience and informational purposes only. We have no control over the nature, content, and availability of those sites. The inclusion of any links does not necessarily imply a recommendation or endorsement of the views expressed within them.
Every effort is made to keep the website up and running smoothly. However, www.serrarigroup.com takes no responsibility for, and will not be liable for, the website being temporarily unavailable due to technical issues beyond our control.
Please note that laws, regulations, and information can change rapidly, and we advise you to conduct further research and seek professional advice when necessary.
By using www.serrarigroup.com, you agree to this disclaimer and its terms. If you do not agree with this disclaimer, please do not use the website.
www.serrarigroup.com, reserves the right to update, modify, or remove any part of this disclaimer without prior notice. It is your responsibility to review this disclaimer periodically for changes.
Serrari Group 2025